
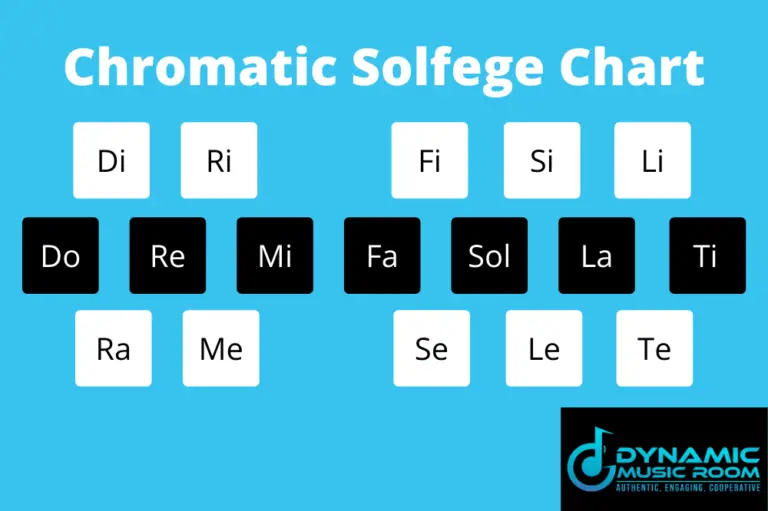
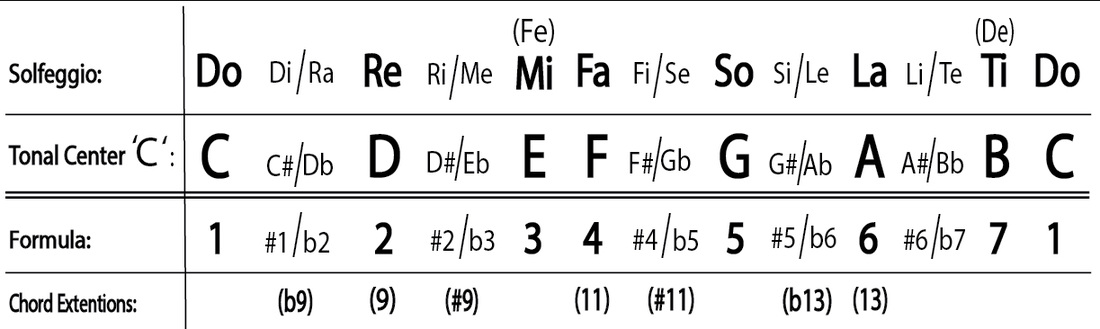
It is called flat because it is 1 half-tone(s) / semitone(s) down from the white note after which is is named – note F. … Another name for Fb is E, which has the same note pitch / sound, which means that the two note names are enharmonic to each other. Since the octave in Western music is normally divided into 12 equal half steps, the characteristic intervals of the diatonic scale can be constructed upon any one of the 12 pitches. For example, if you were to start the chromatic scale on a C, the scale would read as: C, C#, D, D#, E, F, F#, G, G#, A, A#, B, C… and so on. Put simply, the chromatic scale is a musical scale that uses all the musical pitches. Think of the ascending notes as sharps (#) and the descending notes as flats (b). The chromatic solfege scale uses different syllables for the notes going up and coming down. What solfege notes are included in an ascending chromatic scale?
Is solfege so or sol?įrom the dictionaries, it seems like at least in American English, “sol” (as in “do, re, mi, fa, sol”) is always pronounced “sole,” but there’s a spelling variation “so” is pronounced “so”.

So rather than, say, naming a C major scale as C D E F G A B C, you can name it as do re mi fa sol la ti do. It works by assigning a syllable to each note of the musical scale. How do you identify solfege?Īs The Sound of Music hints at, solfeggio or solfege is a method of naming pitches. These are largely the same in minor as they are in major, except for the subtonic (te or ↓^7). Each note of a minor scale is also named with scale-degree names. There are a few new solfège syllables in minor including me (↓^3), le (↓^6) ), and te (↓^7) ). Scale degrees in minor are the same as those in major.

So, we take an octave interval and divide it into twelve distinct pitches. The interval between two notes on the chromatic scale is called a semitone or half-step and two semitones is referred to as a tone or whole step. watch?v=yTGSIMfjjIU” What is the interval between the tones of the chromatic scale? Counting by half steps, an octave includes twelve different pitches, white and black keys together. It is made up entirely of successive half steps, the smallest interval in Western music…. What intervals make a chromatic scale?Īll of the pitches in common use, considered together, constitute the chromatic scale.
SOLFEGE CHROMATIC PLUS
Western music typically uses 12 notes – C, D, E, F, G, A and B, plus five flats and equivalent sharps in between, which are: C sharp/D flat (they’re the same note, just named differently depending on what key signature is being used), D sharp/E flat, F sharp/G flat, G sharp/A flat and A sharp/B flat. There will always be 5 single notes – 5 letter names that are only used once.A letter name may be used twice in a row, but never more than twice in a row.Each letter name is used at least once.The Chromatic Scale must start and end on the same Tonic note.watch?v=4CRZ0XcSD8A” How do you make a chromatic scale? That pattern is the chromatic scale, and it is created by simply ascending (or descending) by half-steps and thus playing all possible pitches. The 12 discrete pitches within an octave are C, C-sharp/D-flat, D, D-sharp/E-flat, E, F, F-sharp/G-flat, G, G-sharp/A-flat, A, A-sharp/B-flat, and B. What is the pattern of a chromatic scale?


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
